About MOPITT

Launch:
Status: Inactive
Measuring atmospheric pollutants with MOPITT
Measurements of Pollution in the Troposphere (MOPITT) is a Canadian-built air pollution monitor aboard NASA's Terra satellite. Launched in and deactivated on , MOPITT remains the longest-running air quality mission in space and the longest operating space mission in Canadian history.
The Terra mission, orbiting Earth at about 700 km above ground, is a collaboration led by NASA, with contributions from the Canadian Space Agency (CSA) and the Japan Aerospace Exploration Agency (JAXA).
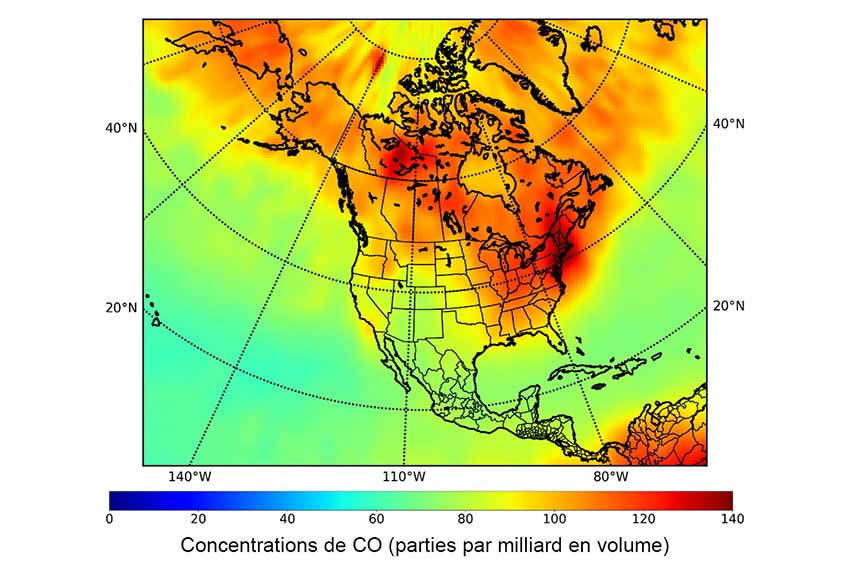
- The CSA provided MOPITT, which delivered vital data on the atmosphere. MOPITT measured carbon monoxide (CO) concentrations in Earth's atmosphere, offering near-global coverage every three days. This data helps scientists identify sources of regional pollution, monitor regional pollution patterns, and track the long-range transport of pollutants.
- JAXA contributed the ASTER instrument, which tracks land surface changes, helping scientists gain a better understanding of our planet.
- NASA was responsible for the satellite's launch and operations, and provided key instruments such as CERES, MISR, and MODIS. These instruments monitor Earth's land, clouds and atmospheric particles, radiation balance, and ocean surface to study climate change, air pollution, and natural disasters.
MOPITT's successes
After becoming operational in , MOPITT gathered high-quality data and has contributed to understanding air quality and improving climate research around the world.
- Research and policy support: MOPITT data allows Canada to study air quality, supports work with other countries to reduce air pollution, and helps scientists better understand climate change. Its CO measurements will continue to be used in United Nations' climate reports and help improve climate models and policies to tackle global environmental problems.
- Wildfires: During the Australian bushfires of –, MOPITT measured record CO levels. It was also crucial in measuring CO emissions from the extreme Canadian wildfires of , highlighting how fires impact air quality and composition, monitor how much carbon is released into the air, and impact our Earth's climate.
- Innovation in monitoring systems: MOPITT data powered Environment and Climate Change Canada's Carbon Assimilation System and has enhanced studies on air pollution trends, wildfire impacts, and emission reductions during the COVID-19 pandemic. It also contributed to advanced atmospheric forecast models, such as those developed by the European Centre for Medium-Range Weather Forecasts, used worldwide.
- Global collaboration: MOPITT data has been used to validate the data from over 30 instruments on 20 satellites, improving 104 atmospheric models developed by more than 1,350 researchers worldwide.
- Climate monitoring: MOPITT's CO measurements continue to be vital to track air quality trends and ozone chemistry – ozone being essential to life on Earth. MOPITT data has revealed global CO decreases since the early , enabling researchers to identify regional trends and compare urban impacts.
MOPITT performed over 2.2 billion atmospheric scans and enabled 50 scientific discoveries. Even though the instrument is now turned off, its data record remains fundamental to studies of environmental pollution, climate modelling, and policy-making worldwide.
Why study carbon monoxide?
Carbon monoxide (CO) is a colourless, odourless toxic gas produced by incomplete combustion, such as vehicle emissions or biomass burning. CO plays a critical role in the chemical processes within the lower atmosphere, impacting air quality and ozone concentrations.
Impact and legacy
Before MOPITT, CO measurements were limited and localized. The instrument's global scans from space provided a detailed picture of CO distribution for the first time and helped scientists understand how natural events and human activities contributed to air pollution. By delivering unprecedented data, MOPITT supported efforts to address pollution, assess antipollution initiatives, and protect both human health and the environment. MOPITT's success highlights Canada's leadership in space-based environmental monitoring.